Grissom Air Reserve Base, Indiana
Origin of current name: Named in honor of Lt Col Virgil Ican ("Gus") Grissom (1926-1967). One of the original seven United States astronauts, Colonel Grissom made the second Project Mercury flight and a Project Gemini flight in July 1961. He died on January 27th 1967 in a fire aboard an Apollo spacecraft under test at the Kennedy Space Center.
Date current name was assigned to base: May 12, 1968
Previous Names: USAF Storage Branch, November 16th 1951; Bunker Hill Air Force Base, June 22nd 1954.
Date Established: July 1, 1942
Date Occupied: June 22, 1954
Construction Began: December 27, 1952
Base Units: 4433d Air Base, April 1st 1955; 323d Air Base Group, August 8th 1955; 4041st Air Base Group, September 1st 1957; 305th Combat Support Group, June 1st 1959-.
Changes in Capability: Hospital completed January 1958; 680-unit Capehart housing project completed December 1958; construction for B-47s and B-58s included runway extension to 12,000 feet, two 1,000 foot overruns, other concrete areas, maintenance docks, and enlargement of operations building, May 1959; five 200-man dormitories completed August 1959; further additions and modifications of concrete areas and structures completed for B-58 operations 1963-1969; EC-135 operations 1969-1970; 200 additional base housing units completed June 30th 1971; SAC (host command) conducted air refueling (KC-135) operations from early 1970s; B-1 in-flight refueling testing conducted 1975; accelerated copilot enrichment program (T-37, T-38) started October 1977; major base heating plant alteration completed June 1980; several buildings constructed and facilities modified to accommodate A-10 operations 1981.
Changes in Status: USAF obtained from USN right of entry to 25 buildings, November 1951; transferred from USN to USAF in inactive status, March 31st 1954; activated August 18th 1955.
History:
Grissom Air Reserve Base is one of only four Air Force Reserve Command bases in the nation. Its history began on July 1, 1942 when it was opened by the U.S. Navy as Bunker Hill Naval Air Station. During the ensuring four years, it served as a training base for thousands of Navy, Marine, and Coast Guard pilots. One of its most famous alumni is former major league baseball star and member of the baseball hall of fame, Ted Williams.
After World War II, the base was closed and the area reverted to its former use as farmland. With the outbreak of the Korean conflict, the base was reopened by the Air Force as Bunker Hill Air Force Base on June 22, 1954. The base was under the direction of the Tactical Air Command and was home to the 4433rd Air Base Squadron and the 323rd Fighter-Bomber Wing.
In 1955, the Air Defense Command's 319th Fighter Interceptor Squadron was added. The Strategic Air Command arrived in the mid-fifties and assumed jurisdiction of the base on September 1, 1957. In May 1959, the 305th Bomb Group and its B-47 aircraft arrived. Later that same year, the first KC-135 Stratotankers were assigned to the base. Two years later, the B-58 "Hustler" bomber began replacing the B-47s.
After 26 years of bearing the name Bunker Hill, the base was renamed on May 12, 1968 in honor of Lieutenant Colonel Virgil I. "Gus" Grissom, a native of Mitchell, Ind. Colonel Grissom was one of America's original seven astronauts and was killed during a fire in his Apollo capsule at Cape Kennedy, Fla. The changes continued and on Jan.1, 1970, the 305th Bomb Group was replaced by the 305th Air Refueling Wing.
Grissom's mission changed from bombers to tankers and the base became one of the largest KC-135 bases in the nation. The Air Force Reserve became part of the Grissom community in 1971 when the 434th Special Operations Wing and its A-37 aircraft relocated to the base. For the next 23 years Grissom was home to both active duty and reserve personnel.
In 1978, a second Air Force Reserve unit--the 931st Air Refueling Group-- joined the scene. At the height of its operations, the base was home to one active duty and two Air Force Reserve wings, 60 KC-135 Stratotankers and 18 A-10 Thunderbolt II fighter aircraft.
Due to changes in the Air Force mission, two units (one reserve, one active duty) were deactivated in 1994. In October of that year, Grissom was realigned as an Air Force Reserve Command facility. Today, the host-unit is the 434th Air Refueling Wing and Grissom is one of only four Air Reserve Bases in the nation.
While the Air Force has the largest contingent of personnel at Grissom, it is also home to organizations from other branches of America's armed forces. The Army Reserve has had a presence at Grissom since the 1970s. A Marine Corps Reserve unit relocated to the base in 2001 and the Navy Reserve added a unit in 2002.
In addition to its contributions to our nation's defense, Grissom Air Reserve Base plays an important part in the local community. It has a combined military-civilian work force and is the largest employer in Miami county and the third largest in north central Indiana. Its annual economic impact is more than $80 million per year. Grissom units are heavily involved in community activities, including the "Toys for Tots" program, and the base was designated as a "Tree City" by the National Arbor Day Foundation.

Bunker Hill Naval Air Station, November 1943
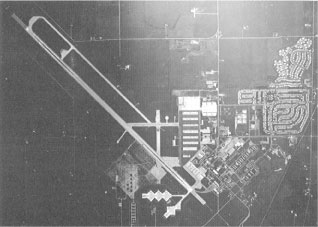
Grissom AFB, 1985